Digital vs. Electronic Signature: Key Differences Explained
Originally published on 18 September 2023. Last updated on 11 August 2025.
As businesses embrace digital transformation, the need for secure and efficient ways to sign documents online has surged. Whether you’re finalizing contracts, onboarding clients, or approving internal documents, electronic and digital signatures have become essential tools in modern workflows.
In fact, the global digital signature market was valued at $4.4 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $42 billion by 2030, according to Straits Research, highlighting just how quickly adoption is growing.
While the terms “digital signature” and “electronic signature” are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between them, explore their unique use cases, and help you determine which solution best fits your organization’s needs.
Understanding the Differences Between Electronic and Digital Signatures
What Is a Wet Signature?
Before exploring the difference between electronic and digital signatures, it’s helpful to understand the traditional method: the wet signature.
A wet signature—also called a handwritten or physical signature—refers to signing a paper document using a pen and ink. Historically, wet signatures were the only accepted method for legally binding agreements and fraud prevention.
But with the rise of digital workflows, organizations are moving away from manual signing. Replacing wet signatures with digital solutions offers a range of benefits:
- Streamlined workflows and reduced paperwork
- Faster document turnaround and fewer delays
- Fewer signing errors
- Increased productivity and reduced admin workload
- Better customer experience
- Improved sustainability by cutting paper usage and eliminating travel for signers
Now, with electronic and digital signatures more accessible than ever, what’s the difference between the two? And which one is right for your business?
Digital Signature vs. Electronic Signature
While often used interchangeably, digital signatures and electronic signatures are not the same. Here’s what sets them apart:
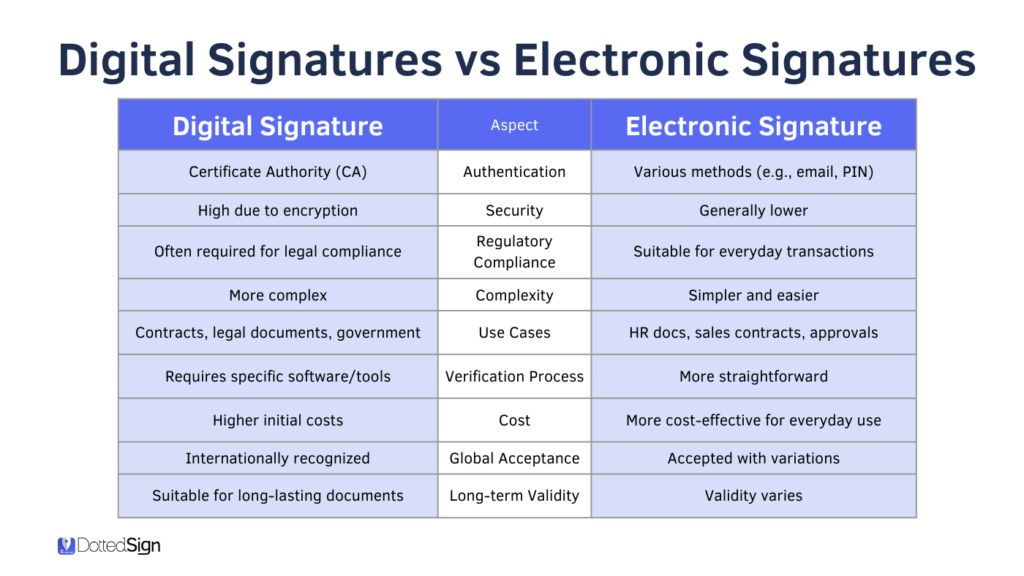
What Is an Electronic Signature?
An electronic signature (e-signature) is a broad term that refers to any electronic method of indicating agreement or approval on a digital document. According to the U.S. E-Sign Act, it is:
“An electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.”
Put simply, an electronic signature is a digital alternative to signing paper documents—used to show consent or approval.
Common examples include:
- Typing your name into a form field
- Signing using a stylus or finger on a touchscreen
- Clicking “I agree” on an online contract
- Inserting a scanned image of your signature
- Entering a PIN for document approval
- Signatures created with e-signature platforms like DottedSign
While electronic signatures are convenient and legally recognized in many countries, they vary in security levels. That’s why industries like finance, healthcare, and legal often require digital signatures for higher assurance.

What Is a Digital Signature?
A digital signature is a specific type of electronic signature that uses advanced encryption technology to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of a digital document.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) defines it as:
“A mathematical algorithm routinely used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message.”
Unlike basic e-signatures, digital signatures use public key infrastructure (PKI) and require identity verification through a trusted third party, known as a Certificate Authority (CA).
How Digital Signatures Work
Digital signatures rely on cryptographic algorithms that generate a unique digital fingerprint, binding the signer’s identity to the document.
Here’s how it works:
- The signer is verified through a digital certificate issued by a Certificate Authority.
- A private key is used to create the signature.
- The document is signed, and the signature is mathematically linked to the content.
- Any tampering or post-signing changes will invalidate the signature.
This process ensures:
- ✅ Authentication: Verifies who signed the document
- ✅ Integrity: Confirms the document wasn’t altered after signing
- ✅ Non-repudiation: Prevents the signer from denying their involvement
Electronic Signature vs. Digital Signature: Key Distinction
💡 All digital signatures are electronic signatures, but not all electronic signatures are digital signatures.
Electronic signatures are ideal for day-to-day business approvals and customer agreements, while digital signatures offer the highest level of trust—critical for legally sensitive or regulated transactions.
What’s the Difference Between Electronic and Digital Signatures?
Although often used interchangeably, electronic signatures and digital signatures serve distinct purposes and offer different levels of security.
Purpose
An electronic signature confirms a signer’s intent to sign and enter an agreement. It’s a broad term encompassing any digital mark, click, or typed name that indicates consent.
A digital signature, however, goes a step further—it uses encryption and digital certificates to verify the authenticity of the document and ensure it hasn’t been altered after signing.
Security
The security level depends on the type of signature used and your industry’s compliance needs.
- Electronic Signature: Offers basic identity verification (e.g., OTPs, email confirmation) and includes an audit trail for accountability.
- Digital Signature: Uses PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) and a digital certificate issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). This binds the signer’s identity to the document and ensures it remains tamper-proof.
If your organization handles sensitive data or operates in a highly regulated field, digital signatures provide the enhanced assurance needed to comply with stricter legal and security standards.
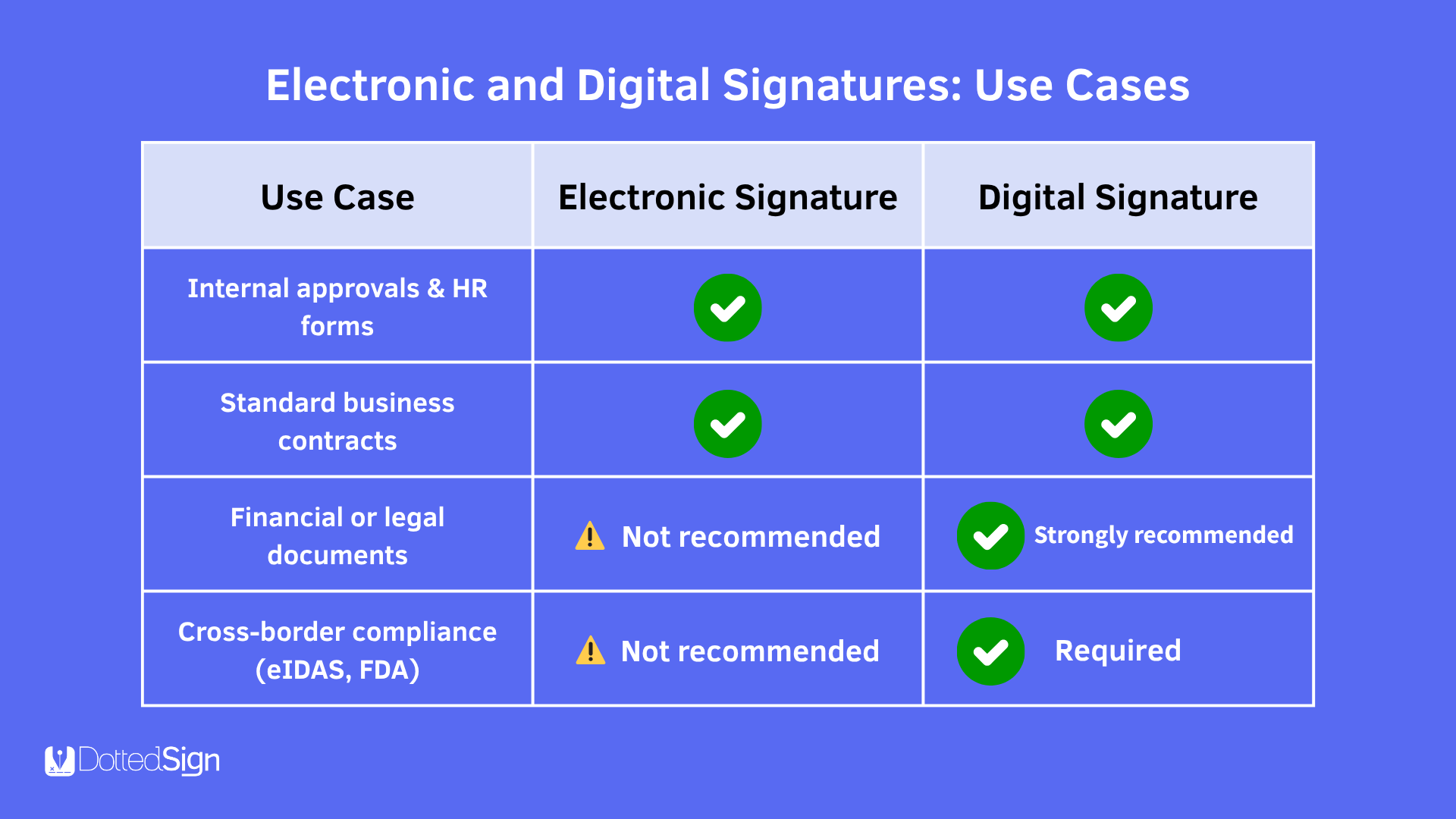
Legal Compliance
Both signature types can be legally binding, but digital signatures offer stronger legal enforceability—especially in international or regulated environments.
U.S. Regulations:
- E-Sign Act (2000)
- UETA (Uniform Electronic Transactions Act)
These laws grant equal legal status to electronic signatures and traditional handwritten ones, as long as there’s:
- Intent to sign
- Consent to use electronic records
- Record retention
- Signature validity
EU Regulation:
- eIDAS Regulation (EU No. 910/2014)
This sets a three-tier signature system:
- Simple Electronic Signature (SES)
- Advanced Electronic Signature (AES)
- Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) – the most secure and legally robust, often backed by digital signatures.
International Regulations
Many countries have adopted unique laws to govern electronic and digital signatures:
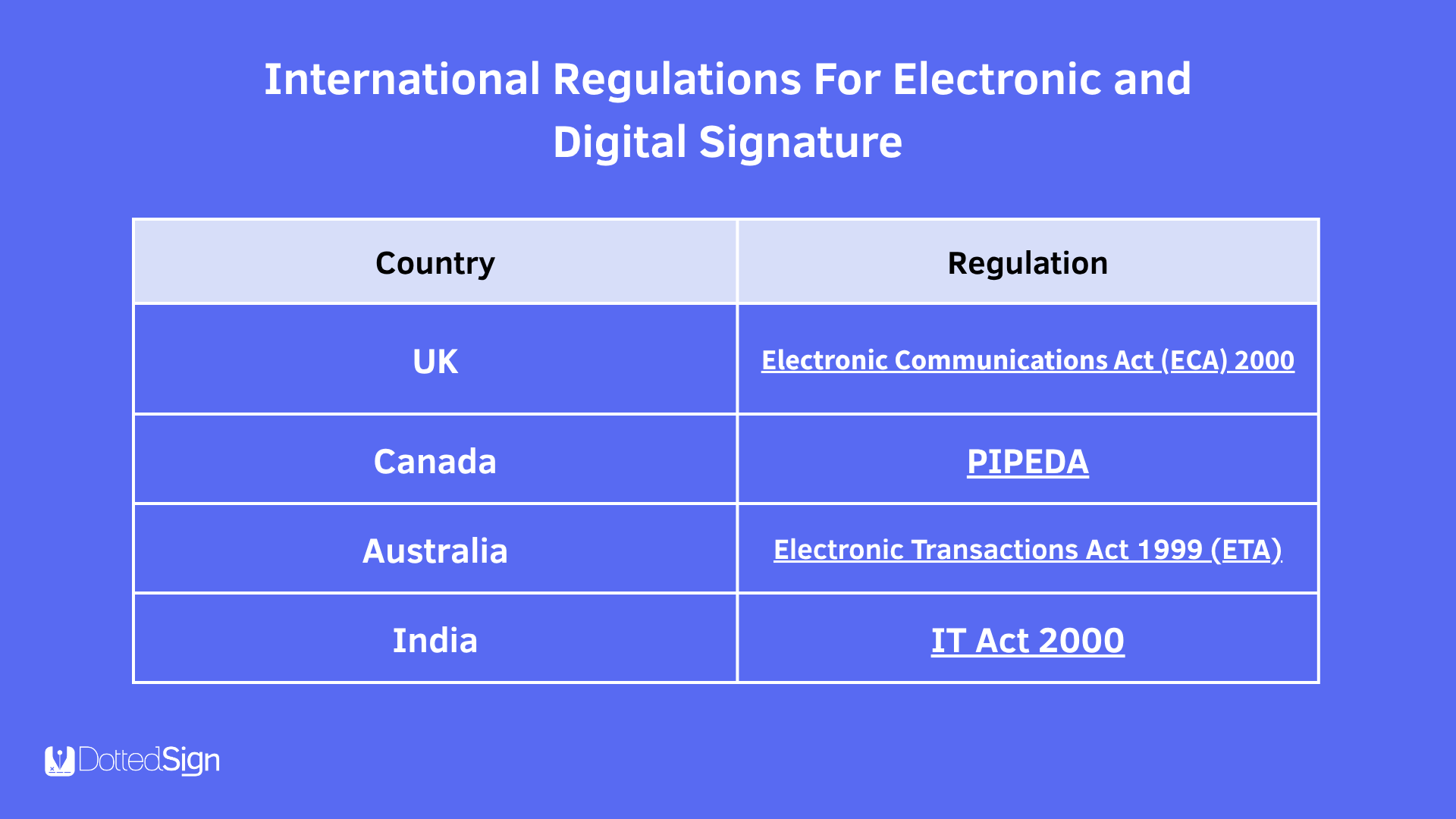
While the legal framework may vary, the core requirements of intent, consent, and authenticity remain central across jurisdictions.
Are Electronic and Digital Signatures Legally Binding?
Yes—both are legally binding in many regions worldwide.
The key is proving intent and consent, often demonstrated by:
- Clicking an “I agree” button
- Typing a name into a form
- Uploading or drawing a signature
To enhance validity, it’s crucial to maintain an audit trail, verify signer identity, and retain signed records in a secure system. Digital signatures like DottedSign take this further by embedding tamper-evident protections and verified identity into the signature itself.
Considering an E-Signature Solution for a Simplified Process
At the end of the day, the most crucial difference between electronic and digital signatures is the level of security they can offer. As the more safeguarded option, digital signatures are often the best choice for organizations across industries. For those pursuing a streamlined document signing process, comprehensive e-signature and workflow solutions like DottedSign can enable their teams to apply digitally certified e-signatures with ease.
Designed for teams of all sizes, this smart, easy-to-adopt solution can help businesses:
- Capture electronic signatures quickly and easily.
- Track documents in real-time.
- Automate document delivery.
- Manage signature tasks.
- Customize organizational branding.
- Improve productivity and business workflows.
- Guarantee a legally binding and secure document signing process.
With valuable integrations, an encrypted process, a detailed audit trail, and advanced security that works across devices, individual users and businesses can ensure a simplified, highly-protected process. Learn more about our robust e-signature solution, and sign up for free to get started today.


